Innovations in Hearing Aid Materials and Design
For people who rely on hearing aids to stay engaged in conversations, work
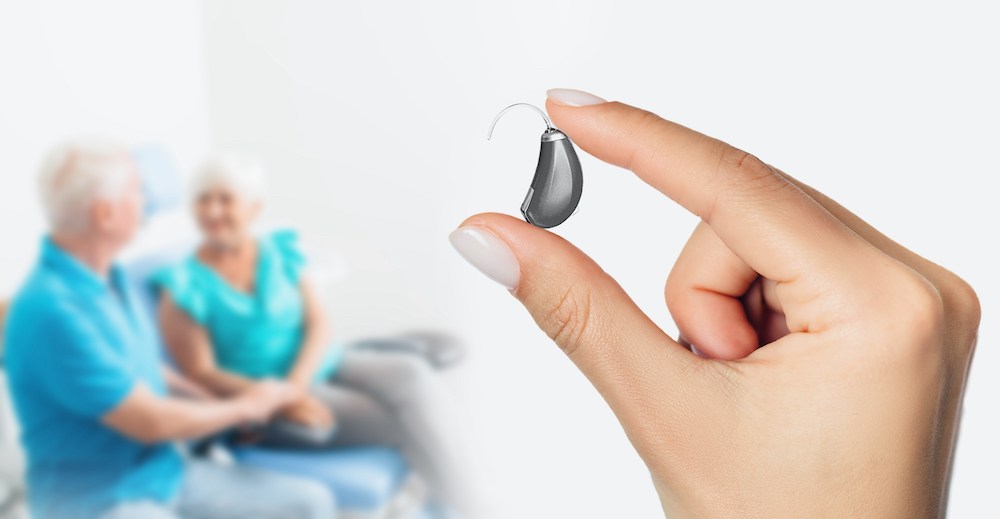
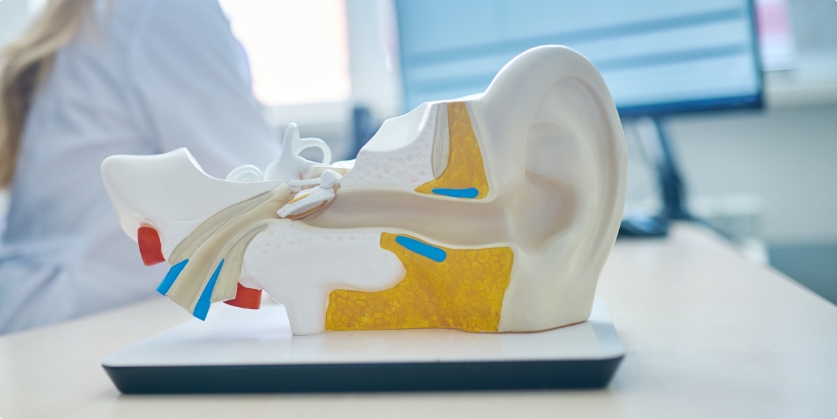

For people who rely on hearing aids to stay engaged in conversations, work

In today’s world, we are constantly surrounded by noise, from traffic
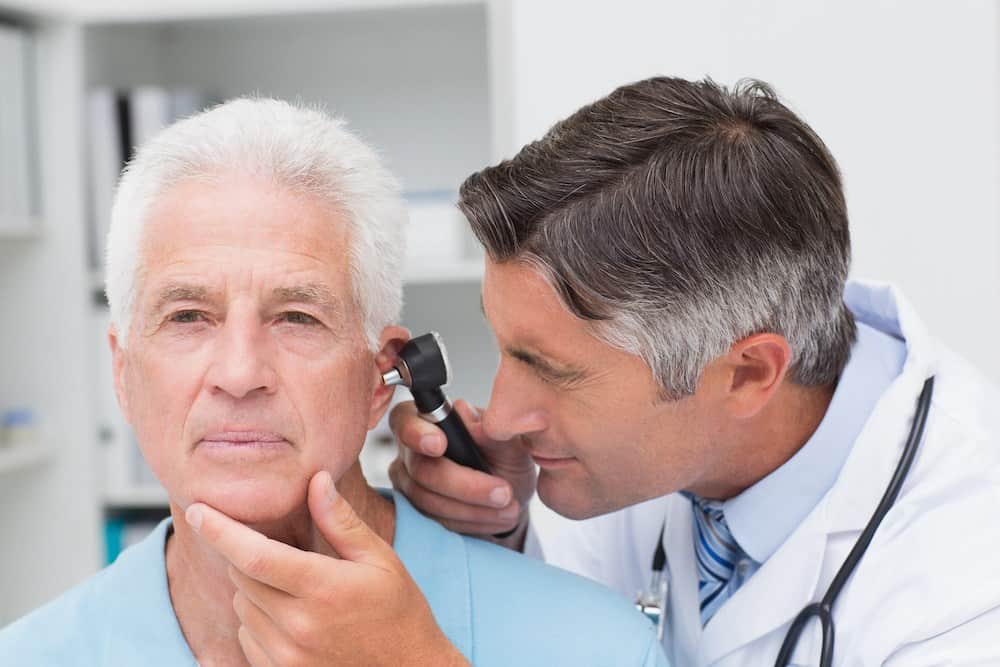
So, you’ve finally decided to book that hearing consultation. Maybe